Understanding the Influence of Artificial Intelligence on the Agriculture Sector.
The increasing global population, projected to
reach 10 billion by 2050, is exerting significant pressure on the agricultural
sector to boost crop production and optimize yields. To address imminent food
shortages, two potential strategies have emerged: expanding land use and
adopting large-scale farming, or embracing innovative practices and harnessing
technological advancements to enhance productivity on existing farmland.
Contribution of AI in Agriculture
The notion of combining AI and agriculture may have
seemed unconventional until recently. Agriculture, a cornerstone of human
civilization for centuries, has provided sustenance and driven economic growth,
while AI, a relatively recent development, emerged only in the past few
decades. However, as with every industry, agriculture is embracing innovation.
In recent years, there have been significant advancements in agricultural
technology, transforming farming methods. These innovations are crucial in
addressing pressing global challenges like climate change, population growth,
and resource scarcity, which threaten the sustainability of our food system.
Integrating AI offers solutions to numerous challenges and mitigates the
drawbacks of traditional farming practices.
Data Based Decision-Making
The contemporary world revolves around data. Agricultural organizations leverage data to gain comprehensive insights into every facet of the farming process, from scrutinizing individual acres of land to monitoring the entire supply chain and delving into the intricacies of yield generation. AI-driven predictive analytics is already revolutionizing agribusinesses, allowing farmers to efficiently gather and process vast amounts of data in minimal time. Moreover, AI aids in analyzing market trends, predicting prices, and identifying optimal timings for planting and harvesting.
In agriculture, artificial intelligence facilitates soil health exploration, provides insights into weather patterns, and recommends the judicious application of fertilizers and pesticides. Farm management software enhances both production and profitability, empowering farmers to make informed decisions at every stage of crop cultivation.
Cost Saving
Enhancing farm yields remains an ongoing
objective for farmers. When paired with AI, precision agriculture offers the
potential for farmers to cultivate more crops using fewer resources. AI
integration in farming amalgamates optimal soil management techniques, variable
rate technology, and efficient data management practices to optimize yields
while curbing expenditure.
The Impact of Automation
Agricultural labor has long been strenuous,
with ongoing challenges of shortages. However, automation offers a remedy
without necessitating additional hires. While mechanization previously
converted arduous tasks once requiring immense human effort and animal labor
into activities achievable within mere hours, a fresh wave of digital
automation is once again reshaping the sector.
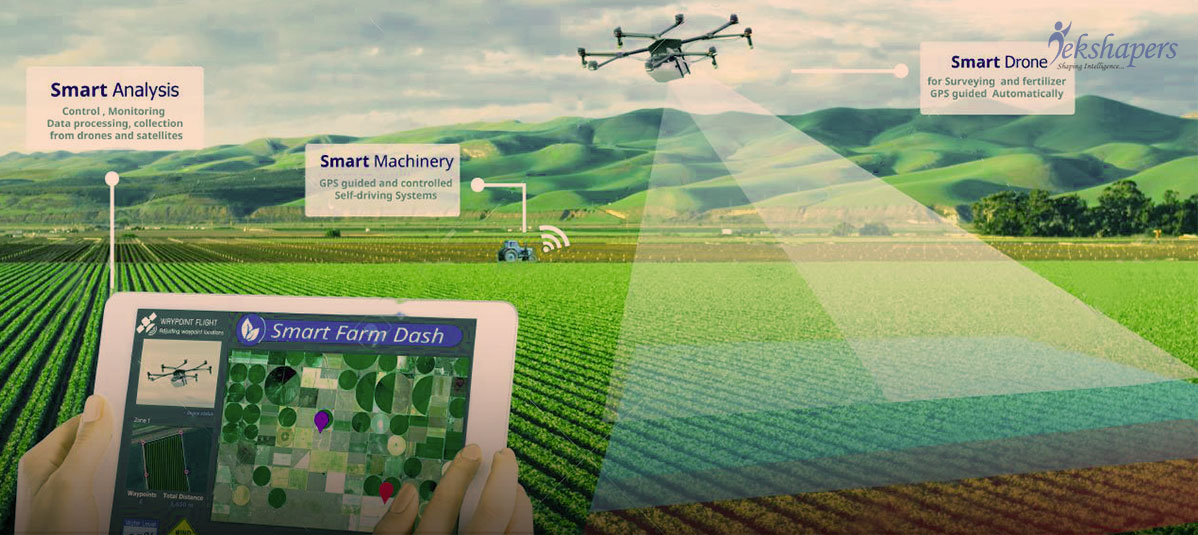
Automated farm equipment, including autonomous
tractors, intelligent irrigation and fertilization systems, IoT-enabled
agricultural drones, precision spraying technology, vertical farming software,
and AI-powered greenhouse robots for harvesting, exemplify this shift. Compared
to human farm workers, AI-driven tools exhibit superior efficiency and
precision.
Applications of AI in agriculture
Artificial intelligence finds numerous
applications in agriculture, with the AI in agriculture market poised for
significant growth from USD 1.7 billion in 2023 to USD 4.7 billion by 2028, as
per MarketsandMarkets.
Optimizing automated irrigation systems
AI algorithms facilitate independent crop
management. When integrated with IoT sensors overseeing soil moisture and
weather, these algorithms dynamically determine optimal irrigation levels in
real-time. This autonomous irrigation system is engineered to preserve water
while advancing sustainable agricultural practices. In smart greenhouses, AI
optimizes plant growth by automatically regulating temperature, humidity, and
light levels using up-to-the-minute data.
AI assumes a pivotal role in identifying leaks
within irrigation systems. Through data analysis, algorithms discern patterns
and irregularities suggestive of potential leaks. Machine learning (ML) models
can be instructed to recognize distinctive leak signatures, like alterations in
water flow or pressure. Timely monitoring and analysis facilitate early
detection, mitigating water wastage and potential crop harm.
Crops and Soil: Quality Supervision
The incorrect blend of nutrients in soil can significantly impact crop health and development. AI-enabled identification of these nutrients and assessment of their effects on crop yield empower farmers to easily enact necessary adjustments.
While human observation is prone to limitations in accuracy, computer vision models can continuously monitor soil conditions, gathering precise data essential for combating crop diseases. This botanical data is then leveraged to evaluate crop health, forecast yields, and flag any specific issues. Plants activate AI systems through sensors detecting their growth conditions, prompting automated environmental adjustments.
Identifying soil quality, crop growth, and the
presence of pests or diseases can all be achieved through computer vision in
agriculture. This technology employs AI to analyze images, identifying mold,
rot, insects, and other threats to crop health. Integrated with alert systems,
it enables swift action by farmers to exterminate pests or isolate affected
crops, thus curbing disease spread.
Yield mapping leverages machine learning algorithms to process extensive datasets in real-time, aiding farmers in comprehending their crop's patterns and attributes for improved planning. Through the integration of methodologies like 3D mapping and data sourced from sensors and drones, farmers can forecast soil yields tailored to individual crops. Data accumulation across multiple drone flights facilitates progressively refined analysis, driven by sophisticated algorithms.
These approaches enable precise predictions of forthcoming yields for specific crops, empowering farmers to strategize optimal seed sowing locations and timing, as well as resource allocation, ensuring maximal return on investment.
Post-Harvest Support
AI serves beyond crop monitoring during growth
stages; it extends its utility to post-harvest activities. While conventional
sorting methods predominantly rely on manual labor, AI offers enhanced
precision in sorting produce.
Ensuring security is another crucial aspect of
farm management, given that farms are frequent targets for burglaries, often
challenging for farmers to monitor continuously. Additionally, animals pose
another threat, be it foxes infiltrating chicken coops or a farmer's livestock
causing damage to crops or equipment.
Difficulties Associated with Applying AI in Agriculture
AI holds great potential to revolutionize
agriculture, but it also presents several challenges:
Data Collection and Quality
AI algorithms require vast amounts of data to
train effectively. However, in agriculture, data collection can be challenging
due to factors like remote locations, lack of connectivity, and varying data
formats. Ensuring data quality and consistency across different sources is also
a significant challenge.
Interpretability and Transparency
AI algorithms often operate as "black
boxes," meaning it can be difficult to understand how they arrive at their
conclusions. In agriculture, where decisions can have significant economic and
environmental impacts, it's crucial to have transparent and interpretable AI
models.
Adaptability to Local Conditions
Agricultural practices vary greatly from region
to region due to differences in climate, soil, crops, and farming techniques.
Developing AI models that can adapt to these local conditions and provide
relevant insights is a complex challenge.
Access and Affordability
While AI technologies have the potential to
increase agricultural productivity and profitability, there are concerns about
access and affordability, particularly for smallholder farmers in developing
countries. Ensuring that AI solutions are accessible and affordable to all
farmers is essential for equitable agricultural development.
Ethical Considerations
AI in agriculture raises ethical concerns
related to data privacy, ownership, and algorithmic bias. There's a need to
establish ethical guidelines and regulations to ensure that AI technologies are
developed and deployed responsibly in agriculture.
Infrastructure and Connectivity
Many agricultural regions lack the necessary
infrastructure and connectivity to support AI technologies. Improving access to
electricity, internet connectivity, and computing resources is essential for
the widespread adoption of AI in agriculture.
Skill Gap
Implementing AI technologies in agriculture
requires specialized knowledge and skills. Farmers and agricultural workers may
need training to understand how to use AI tools effectively and interpret the
insights they provide.
Addressing these challenges will require
collaboration among farmers, researchers, policymakers, and technology
developers to ensure that AI contributes positively to the sustainability and
productivity of agriculture.
Conclusion
AI is poised to assume an increasingly
significant role in agriculture and the pursuit of food sustainability in the
years ahead. Throughout history, technology has continuously propelled
agriculture forward, evolving from rudimentary tools and irrigation to tractors
and now AI. Each advancement has enhanced efficiency while mitigating the
challenges faced by farmers.
Entitled "AI in Agriculture — Shaping the Future of Farming," this shift is underpinned by the undeniable advantages AI offers. Smart farming tools, automated processes, and AI-driven products streamline repetitive tasks, enabling human workers to focus on strategic activities requiring their judgment. The accessibility of computer vision and agricultural robotics is expected to expedite AI's integration into farming practices.
Sources: Sources: intellias.com, wikipedia.com, linkedin.com, sical.ac.in, fsii.in, tekshapers.com, weloveai.ca, bitsathy.ac.in, market.us, analyticsweek.com.
Compiled by Shorya Bisht