The role and influence of AI in addressing, combating and
predicting natural calamities.
Natural calamities, spanning from hurricanes
and earthquakes to wildfires and floods, have inflicted widespread devastation
on our planet for centuries. These catastrophic occurrences result in
incalculable loss of life and property, often leaving communities in ruins.
While we cannot entirely prevent or accurately predict these events, leveraging
technology and innovation offers avenues to mitigate their impact. Artificial
Intelligence (AI) is emerging as a powerful tool in disaster prevention, early
warning systems, and response strategies.
Before exploring how AI can aid in disaster prevention, it's essential to grasp the diversity of these phenomena. Natural disasters encompass geological, meteorological, hydrological, and climatological events. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and tsunamis fall within geological disasters, while meteorological events include hurricanes, tornadoes, and blizzards. Hydrological disasters involve floods and landslides, while climatological disasters encompass droughts, heatwaves, and wildfires.
The Imperative for Prevention
Although natural disasters are inherently
unpredictable, their impacts can be mitigated through early intervention and
effective preparedness. Given their potential for devastating economic, social,
and environmental consequences, preventing these disasters or minimizing their
effects is imperative on a global scale. AI, with its capacity to process
extensive data, discern patterns, and offer real-time predictions, is
revolutionizing disaster prevention efforts.
Critical to disaster prevention is the
provision of early warnings to vulnerable populations. AI-driven systems can
analyze data from diverse sources, including weather sensors, satellites, and
social media, to detect early indicators of impending disasters. For instance,
in the case of hurricanes, AI algorithms can analyze atmospheric data to
accurately predict their trajectory and intensity. These predictions enable
authorities to issue timely warnings and facilitate the evacuation of at-risk
areas, potentially saving countless lives.
Seismic Activity Prediction
AI facilitates a better understanding and
prediction of earthquakes. Machine learning models analyze historical seismic
data, monitor ground movements, and detect subtle changes in the Earth's crust
to anticipate seismic events. While earthquakes may not be preventable, early
detection allows people precious seconds or minutes to seek cover, potentially
reducing casualties.
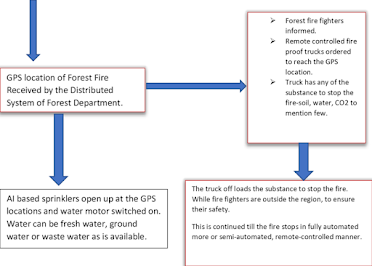
Forest Fire Prevention
AI-powered systems play a crucial role in
preventing wildfires, which have been increasing in frequency and intensity due
to climate change. Drones equipped with AI algorithms can monitor forests for
potential ignition sources, such as lightning strikes or campfires. AI can also
analyze weather conditions to predict fire spread, enabling firefighters to
strategize their efforts effectively.
Flood Prediction and Management
Floods, a recurrent disaster, affect numerous
regions globally. AI models process data from rainfall gauges, river levels,
and soil moisture sensors to predict when and where floods are likely to occur.
Additionally, AI-driven flood modeling informs better infrastructure design and
urban planning to reduce flood risk and damage.
Landslides, often following heavy rainfall or
earthquakes, pose significant threats to communities in hilly or mountainous
regions. AI-based geospatial analysis identifies landslide-prone areas and
issues early warnings. These systems rely on satellite data, ground sensors,
and historical landslide events to pinpoint at-risk locations.
While not directly preventing disasters, AI
contributes to mitigating climate change, the root cause of many natural
calamities. Machine learning algorithms analyze climate data, identify trends,
and develop strategies for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. AI optimizes
energy usage, promotes renewable energy sources, and supports sustainable land
use practices.
Disaster Response Coordination
AI enhances the coordination of disaster
response efforts. Chatbots, virtual assistants, and automated systems
streamline communication among emergency responders, government agencies, and
affected populations. Real-time data analysis assesses the disaster's scope and
optimizes resource allocation.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While AI holds promise in disaster prevention,
it presents complex challenges and ethical considerations that require careful
attention.
Data Privacy and Security
AI relies on extensive data, raising concerns
about privacy and security. Data collection from various sources, including
personal devices and sensors, necessitates safeguarding individuals' privacy
and protecting against cyber threats.
Bias in AI
AI algorithms can inherit biases from training
data, potentially resulting in inaccurate predictions or unfair resource
allocation. Addressing bias requires careful data selection, preprocessing, and
ongoing monitoring of AI models.
Accessibility and Equity
Ensuring equitable access to AI-driven disaster
prevention tools is essential, particularly for historically disadvantaged
communities with limited resources and infrastructure.
Accountability and Decision-Making
Clear lines of accountability and transparent
decision-making processes are vital as AI becomes integral to disaster
prevention efforts.
Overreliance on Technology
Balancing AI-assisted decision-making with
human expertise is critical to avoiding overreliance on technology.
Infrastructure and Resource Constraints
Addressing infrastructure and resource
disparities is necessary to ensure global accessibility to AI-driven disaster
prevention technologies.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is transforming
disaster prevention and management, offering powerful capabilities to predict,
prepare for, and respond to natural calamities effectively. Careful
consideration of ethical concerns and equitable access to AI technologies are
essential as we harness its potential to protect communities and our planet
from the impacts of natural disasters.
Sources: .bbvaopenmind.com, nps.gov, researchgate.net, sciencedirect.com, nature.com,linkedin.com,mdpi.com
Compiled by: Shorya Bisht
Data Scientist







No comments:
Post a Comment